REVIEW
Interactions between entomopathogenic nematodes and entomopathogenic fungi in the aspect of new possibilities for biological plant protection
1
Department of Biological Methods, Institute of Plant Protection – National Research Institute, Poznań, Poland
These authors had equal contribution to this work
A - Research concept and design; B - Collection and/or assembly of data; C - Data analysis and interpretation; D - Writing the article; E - Critical revision of the article; F - Final approval of article
Submission date: 2024-09-27
Acceptance date: 2025-01-10
Online publication date: 2025-09-08
Corresponding author
Katarzyna Barszczewska
Department of Biological Methods, Institute of Plant Protection – National Research Institute, Poznań, Poland
Department of Biological Methods, Institute of Plant Protection – National Research Institute, Poznań, Poland
Journal of Plant Protection Research 2025;65(3):303-310
HIGHLIGHTS
- Occurrence of interactions between fungi and entomopathogenic nematodes
- Biopreparations to reduce the use of chemicals
- The combination of EPN and EPF can be an effective method of pest control
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Entomopathogenic fungi (EPF) and entomopathogenic nematodes (EPNs) have a strategic
and important role in the biological control of agrophages. Micro- and macro-organisms
have become an alternative to chemical methods, not only reducing the use of chemical
pesticides, but also preventing agrophages from becoming resistant to chemicals and minimizing
risks to human, animal and environmental health. The common habitat of EPNs
and EPF is the soil, but interactions between them have mainly been studied in the laboratory.
Recently, there has been a growing interest in combining biological control agents to
increase their efficacy, and many studies have focused on combining EPF and EPNs against
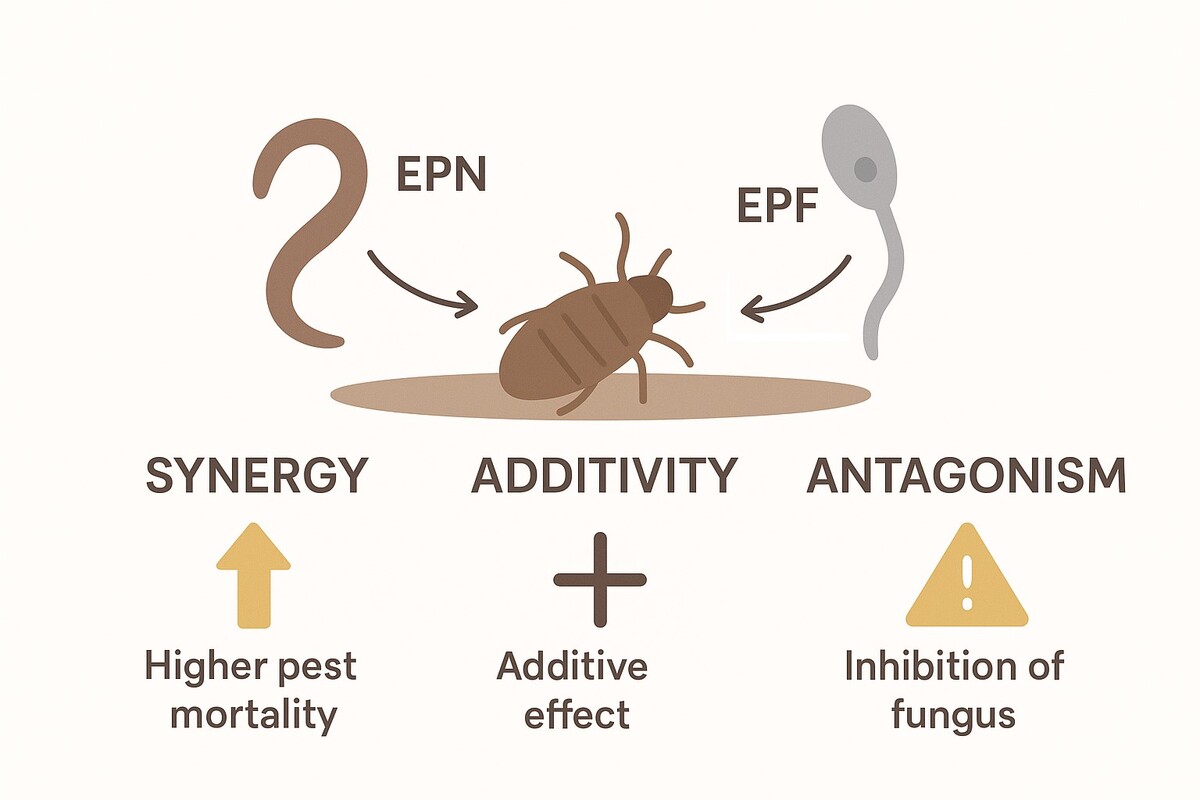
different insect pests. Studies have shown synergistic, additive or antagonistic effects. The
results of these interactions depend on the pathogen, the host species, the different times
of infection and the choice of the appropriate pathogen dose. The aim of this review was to
summarize the existing knowledge on the life cycle of nematodes and the mechanisms of
action of EPF and their application in practice, as well as the interaction between EPNs and
EPF in plant protection against insect pests.
RESPONSIBLE EDITOR
Jolanta Kowalska
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have declared that no conflict of interests exist.
REFERENCES (54)
1.
Abdul Qayyum M., Bilal H., Naeem Ullah U., Ali H., Raza H., Wajid M. 2021. Factors affecting the epizootics of entomopathogenic fungi – a review. Journal of Bioresource Management 8 (4): 78–85. DOI: 10.35691/JBM.1202.0204.
2.
Aghaeepour S., Zibaee A., Ramzi S., Hoda H. 2023. Changes in life table parameters and intermediary metabolism of Cryptolaemus montrouzieri Mulsant after infection by Beauveria bassiana. Journal of Plant Protection Research 63 (1): 68–82. DOI: 10.24425/jppr.2023.144503.
3.
Ansari M.A., Shah F.A., Tirry L., Moens M. 2006. Field trials against Hoplia philanthus (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) with a combination of an entomopathogenic nematode and the fungus Metarhizium anisopliae CLO 53. Biological Control 39 (3): 453–459. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2006.07.004.
4.
Ansari M.A., Tirry L., Moens M. 2004. Interaction between Metarhizium anisopliae CLO 53 and entomopathogenic nematodes for the control of Hoplia philanthus. Biological Control 31 (2): 172–180. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2004.04.002.
5.
Ansari M.A., Shah F.A., Butt T.M. 2008. Combined use of entomopathogenic nematodes and Metarhizium anisopliae as a new approach for black vine weevil, Otiorhynchus sulcatus, control. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata 129 (3): 340–347. DOI: 10.1111/j.1570-7458.2008. 00783.x.
6.
Araújo J.P.M., Hughes D.P. 2016. Chapter one - diversity of entomopathogenic fungi: which groups conquered the insect body? Advances in Genetics 94: 1–39. DOI: 10.1016/bs.adgen.2016.01.001.
7.
Askary T.H., Ahmad M.J. 2017. Entomopathogenic nematodes: mass production, formulation, and application. p. 261–286. In: “Biocontrol agents: entomopathogenic and slug parasitic nematodes” (Abd-Elgawad M.M.M., Askary T.H., Coupland J., eds.). CABI, UK.
8.
Bałazy S., Miętkiewski R., Tkaczuk C., Wegensteiner R., Wrzosek M. 2008. Diversity of acaropathogenic fungi in Poland and other European countries. Experimental and Applied Acarology 46 (1): 53–70.
9.
Barbercheck M.E., Kaya H.K. 1991. Competitive interactions between entomopathogenic nematodes and Beauveria bassiana (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) in soilborne larvae of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Environmental Entomology 20 (2): 707–712. DOI: 10.1093/ee/20.2.707.
10.
Bueno-Pallero F. Á., Blanco-Pérez R., Dionísio L., Campos-Herrera R. 2018. Simultaneous exposure of nematophagous fungi, entomopathogenic nematodes and entomopathogenic fungi can modulate belowground insect pest control. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology 154: 85–94. DOI: 10.1016/j.jip.2018.04.004.
11.
Collier T., Van Steenwyk R. 2004. A critical evaluation of augmentative biological control. Biological Control 31 (2): 245–256. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2004.05.001.
12.
Correa-Cuadros J.P., Sáenz-Aponte A., Rodríguez-Bocanegra M.X. 2016. In vitro interaction of Metarhizium anisopliae Ma9236 and Beauveria bassiana Bb9205 with Heterorhabditis bacteriophora HNI0100 for the control of Plutella xylostella. SpringerPlus 5: 1–8. DOI: 10.1186/s40064-016-3745-5.
13.
Dannon H.F., Dannon A.E., Douro-Kpindou O.K., Zinsou A.V., Houndete A.T., Toffa-Mehinto J., Elegbede I.A.T.M., Olou B.D., Tamò M. 2020. Toward the efficient use of Beauveria bassiana in integrated cotton insect pest management. Journal of Cotton Research 3: 1–21. DOI: 10.1186/s42397-020-00061-5.
14.
Ehlers R.U. 2007. Nematodes: from Science to Commercial Use. p. 135–151. In: “Biological control: a global perspective: case studies from around the world” (C. Vincent, M.S. Goettel, G. Lazarovits, eds.). CABI International. Kiel, Germany, 24118 pp.
15.
Ekbom B.S. 1979. Investigations on the potential of a parasitic fungus Verticillium lecanii for biological control of the greenhouse whitefly (Trialeurodes vaporariorum). Swedish Journal of Agriculturae Research 9: 129–138.
16.
Gadd G.M. 2007. Geomycology: biogeochemical transformations of rocks, minerals, metals, and radionuclides by fungi, bioweathering and bioremediation. Mycological Research 111 (1): 3–49. DOI: 10.1016/j.mycres.2006.12.001.
17.
Gaugler R., Kaya H.K. 1990. Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Biological Control. Boca Raton, CRC Press, FL, USA.
18.
Gaugler R. 2002. Entomopathogenic Nematology. CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 388 pp.
19.
Gul H.T., Saeed S., Khan F.Z.A. 2014. Entomopathogenic fungi as effective insect pest management tactic: a review. Applied Sciences and Business Economics 1 (1): 10–18.
20.
Gullino M. L., Albajes R., Al-Jboory I., Angelotti F., Chakraborty S., Garrett K.A., Hurley B. P., Juroszek P., Makkouk K., Pan X., Stephenson T. 2021. Scientific review of the impact of climate change on plant pests – A global challenge to prevent and mitigate plant pest risks in agriculture, forestry, and ecosystems. IPPC Secretariat. Rome, Italy. DOI: 10.4060/cb4769en.
21.
Kidanu S., Hagos L. 2020. Research and application of entomopathogenic fungi as pest management option: a review. Journal of Environment and Earth Science 10 (3): 31–39. DOI: 10.7176/JEES/10-3-03.
22.
Koppenhöfer H.S., Gaugler R. 2009. Entomopathogenic nematode and bacteria mutualism. p. 99–116. In: “Defensive Mutualism in Microbial Symbiosis” (J .White, M. Torres, eds.). CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA.
23.
Kruk K., Dzięgielewska M. 2019. Wykorzystanie nicieni owadobójczych w biologicznej ochronie roślin. [The use of enthomopathogenic nematodes in biological plant protection]. Młodzi Naukowcy 11: 72–76.
24.
Kuźniar T., Ropek D., Kulig B. 2014. Wykorzystanie grzyba owadobójczego Isaria fumosorosea do zwalczania szkodników w uprawie bobiku. Proceedings of ECOpole 8 (1): 201–207. DOI: 10.2429/proc.2014.8(1)026.
25.
Lalitha K., Karthi S., Vengateswari G., Karthikraja R., Perumal P., Shivakumar MS. 2018. Effect of entomopathogenic nematode of Heterorhabditis indica infection on immune and antioxidant system in lepidopteran pest Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Journal of Parasitic Diseases 42 (2): 204–211. DOI: 10.1007/s12639-018-0983-1.
26.
Liao C., Gao A., Li B., Wang M., Shan L. 2017. Two symbiotic bacteria of the entomopathogenic nematode Heterorhabditis spp. against Galleria mellonella. Toxicon 127: 85–89. DOI: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.11.257.
27.
Litwin A., Nowak M., Różalska S. 2020. Entomopathogenic fungi: unconventional applications. Reviews in Environmental Science and Biotechnology 19: 23–42. DOI: 10.1007/s11157-020-09525-1.
28.
Mudgal S., Toni A., Tostivint C., Hokkanen H., Chandler D. 2013. Scientific support, literature review and data collection and analysis for risk assessment on microbial organisms used as active substance in plant protection products – Lot 1 Environmental Risk characterization. EFSA Supporting Publication 2013, 149 pp. DOI: 10.2903/sp.efsa. 2013.EN-518.
29.
Oliveira-Hofman C., Kaplan F., Stevens G., Lewis E., Wu S., Alborn H.T., Shapiro-Ilan D.I. 2019. Pheromone extracts act as boosters for entomopathogenic nematodes efficacy. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology 164: 38–42. DOI: 10.1016/j.jip.2019.04.008.
30.
Otsuki H., Yano S. 2014. Functionally different predators break down antipredator defenses of spider mites. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata 151 (1): 27–33. DOI: 10.1111/eea.12164.
31.
Ownley B.H., Griffin M.R., Klingeman W.E., Gwinn K.D., Moulton J.K., Pereira R.M. 2008. Beauveria bassiana: endophytic colonization and plant disease control. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology 98: 267–270. DOI: 10.1016/j.jip.2008.01.010.
32.
Park Y., Herbert E.E., Cowles C.E., Cowles K.N., Menard M.L., Orchard S.S., Goodrich‐Blair H. 2007. Clonal variation in Xenorhabdus nematophila virulence and suppression of Manduca sexta immunity. Cellular Microbiology 9 (3): 645–656.. DOI: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2006. 00815.x.
33.
Pell J.K., Hannam J.J., Steinkraus D.C. 2010. Conservation biological control using fungal entomopathogens. BioControl 55 (1): 187–198. DOI:10.1007/s10526-009-9245-6.
34.
Poinar G.O. 2018. Nematodes for Biological Control of Insects. CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 289 pp.
35.
Premanandh J. 2011. Factors affecting food security and contribution of modern technologies in food sustainability. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 91 (15): 2707–2714. DOI: 10.1002/jsfa.4666.
36.
Půža V., Tarasco E. 2023. Interactions between entomopathogenic fungi and entomopathogenic nematodes. Microorganisms 11 (1): 163. DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11010163.
37.
Quesada-Moraga E., Yousef-Naef M., Garrido-Jurado I. Advances in the use of entomopathogenic fungi as biopesticides in suppressing crop pests. p. 63–98. In: “Biopesticides for Sustainable Agriculture” (N. Brich, T. Glare, eds.). Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing: Cambridge, UK.
38.
Sánchez-Gómez T., Harte S.J., Zamora P., Bareyre M., Díez J.J., Herrero B., Niño-Sánchez J., Martín-García J. 2023. Nematicidal effect of Beauveria species and the mycotoxin beauvericin against pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Frontiers in Forests and Global Change 6: 1229456. DOI: 10.3389/ffgc.2023.1229456.
39.
Savary S., Willocquet L., Pethybridge S.J., Esker P., McRoberts N., Nelson A. 2019. The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops. Nature Ecology and Evolution 3: 430–439. DOI: 10.1038/s41559-018-0793-y.
40.
Shapiro-Ilan D, Hazir S, Glazer I. 2020. Advances in use of entomopathogenic nematodes in integrated pest management. In: “Integrated management of insect pests: current and future developments” (M. Kogan, E.A. Heinrichs, eds.). Burleigh Dodds Science Publication, UK, 30 pp.
41.
Shapiro-Ilan D.I., Jackson M., Reilly C.C., Hotchkiss M.W. 2004. Effects of combining an entomopathogenic fungi or bacterium with entomopathogenic nematodes on mortality of Curculio caryae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Biological Control 30 (1): 119–126. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2003.09.014.
42.
Sharapova I.E. 2019. Prospects of using entomopathogenic fungus in development of a biopesticide product with nematicidal activity. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology 19: 101098. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101098.
43.
Shaurub E.S.H. 2023. Review of entomopathogenic fungi and nematodes as biological control agents of tephritid fruit flies: current status and a future vision. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata 171 (1): 17–34. DOI: 10.1111/eea.13244.
44.
Singkaravanit S., Kinoshita H., Ihara F., Nihira T. 2010. Cloning and functional analysis of the second geranyl diphosphate synthase gene influencing helvolic acid biosynthesis in Metarhizium anisopliae. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 87 (3): 1077–1088. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-010-2556-9.
45.
Spescha A., Weibel J., Wyser L., Brunner M., Hermida M.H., Moix A., Scheibler F., Guyer A., Campos-Herrera R., Grabenweger G., Maurhofer M. 2023. Combining entomopathogenic Pseudomonas bacteria, nematodes and fungi for biological control of a below-ground insect pest. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 348: 108414. DOI: 10.1016/j.agee.2023.108414.
46.
Strasser H., Abendstein D., Stuppner H., Butt T.M. 2000. Monitoring the distribution of secondary metabolites produced by the entomogenous fungus Beauveria brongniartii with particular reference to oosporein. Mycological Research 104 (10): 1227–1233. DOI: 10.1017/S0953756200002963.
47.
Swathy K., Parmar M.K., Vivekanandhan P. 2024. Biocontrol efficacy of entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana conidia against agricultural insect pests. Environmental Quality Management 34 (1): e22174. DOI: 10.1002/tqem.22174.
48.
Tarasco E., Santiago Alvarez C., Triggiani O., Quesada Moraga E. 2011. Laboratory studies on the competition for insect haemocoel between Beauveria bassiana and Steinernema ichnusae recovered in the same ecological niche. Biocontrol Science and Technology 21 (6): 693–704. DOI: 10.1080/09583157.2011.570428.
49.
Thambugala K.M., Daranagama D.A., Philips A.J.L., Kannangara S.D., Promputtha I. 2020. Fungi vs. Fungi in biocontrol: an overview of fungal antagonists applied against fungal plant pathogens. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 10: 604923. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.604923.
50.
Torrini G., Mazza G., Carletti B., Benvenuti C., Roversi P.F., Fanelli E., De Luca F., Troccoli A. and Tarasco E. 2015. Oscheius onirici sp. n. (Nematoda: Rhabditidae): a new entomopathogenic nematode from an Italian cave. Zootaxa 3937 (3): 533–548. DOI:10.11646/zootaxa.3937.3.6.
51.
Toth S., Toepfer S., Szalai M., Kiss J. 2022. Limited influence of abiotic and biotic factors on the efficacy of soil insecticides and entomopathogenic nematodes when managing the maize pest Diabrotica v. virgifera (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Agronomy 12 (11): 2697. DOI: 10.3390/agronomy12112697.
52.
Usman M., Gulzar S., Wakil S., Wu S., Piñero J.C., Leskey T.C., Nixon L.J., Oliveira-Hofman C., Toews M.D., Shapiro-Ilan D. 2020. Virulence of entomopathogenic fungi to Rhagoletis pomonella (Diptera: Tephritidae) and interactions with entomopathogenic nematodes. Journal of Economic Entomology 113 (6): 2627–2633. DOI: 10.1093/jee/toaa209.
53.
Vilcinskas A., Matha V., Götz P. 1997. Effects of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae and its secondary metabolites on morphology and cytoskeleton of plasmacytes isolated from the greater wax moth, Galleria mellonella. Journal of Insect Physiology 43 (12): 1149–1159. DOI: 10.1016/S0022-1910(97)00066-8.
54.
Wakil W., Yasin M., Shapiro-Ilan D. 2017. Effects of single and combined applications of entomopathogenic fungi and nematodes against Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier). Scientific Reports 7 (1): 5971. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-05615-3.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.