REVIEW
Climate change and plant protection: challenges and innovations in disease forecasting systems in developing countries
1
Sustainable Agriculture, Nelson Mandela African Institution of Science and Technology, Tengeru, Arusha, Tanzania
A - Research concept and design; B - Collection and/or assembly of data; C - Data analysis and interpretation; D - Writing the article; E - Critical revision of the article; F - Final approval of article
Submission date: 2024-08-01
Acceptance date: 2024-11-25
Online publication date: 2025-07-02
Corresponding author
Agatha Amnaay Aloyce
Sustainable Agriculture, Nelson Mandela African Institution of Science and Technology, Tengeru, Arusha, Tanzania
Sustainable Agriculture, Nelson Mandela African Institution of Science and Technology, Tengeru, Arusha, Tanzania
Journal of Plant Protection Research 2025;65(2):174-186
HIGHLIGHTS
- Abiotic and biotic Stresses
- Adaptation Strategies
- Digital Technologies
- Early Warning Systems
- Host-Pathogen Interactions
KEYWORDS
adaptation strategiesbiotic and abiotic stressesdigital technologiesearly warning systemsfood securityhost-pathogen interactions
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Plant disease forecasting plays a crucial role in managing outbreaks and mitigating economic
and health impacts, thereby contributing significantly to plant protection efforts.
This proactive approach assesses the likelihood of disease outbreaks and increases in disease
intensity, enabling timely intervention and resource optimization. However, climate
change exacerbates this challenge by altering pathogen evolution and host-pathogen interactions,
fostering the emergence of new pathogenic strains, shifting pathogen ranges, and
expanding the geographic spread of plant diseases. In developing countries, these changes
are compounded by limited resources and inadequate infrastructure, creating significant
challenges for forecasting systems and plant protection efforts. The primary objective of
this review was to assess the impact of climate change on plant disease forecasting systems,
with a focus on biotic and abiotic stresses such as temperature changes, altered precipitation
patterns, and extreme weather events. A systematic literature review was conducted using
databases such as PubMed, Web of Science, and Google Scholar, selecting peer-reviewed
studies published between 2020 and 2024. Key data on research objectives, methodologies,
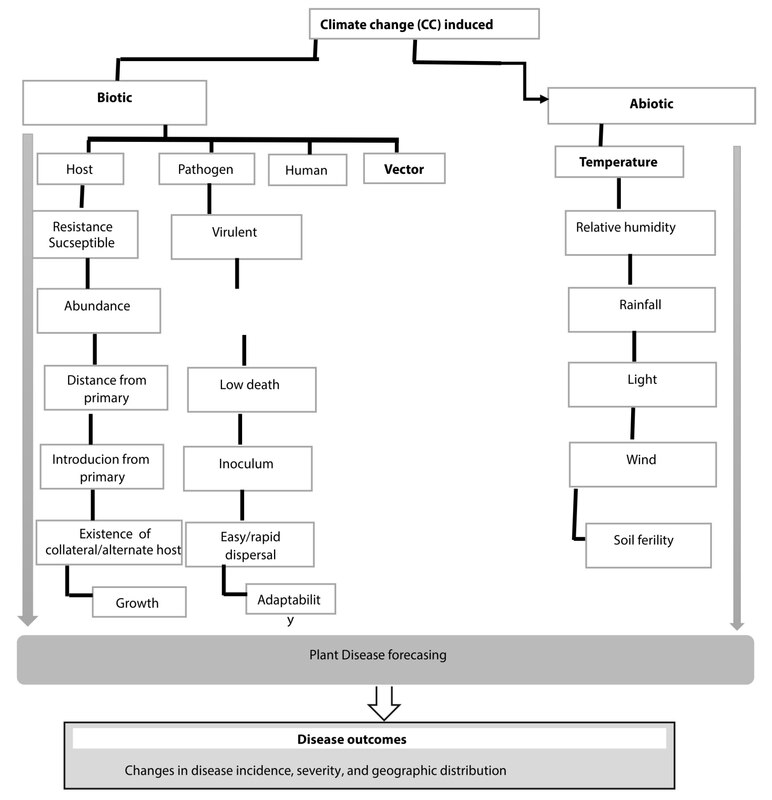
results, and implications were extracted and synthesized, demonstrating how climateinduced
stresses affect components of the disease tetrahedron, including host susceptibility,
pathogen virulence, environmental conditions, and vector dynamics. The findings reveal
that climate change significantly affects forecasting systems and plant protection strategies,
emphasizing the need for reliable, and cost-effective forecasting models adaptable to
diverse and evolving climate conditions, especially in resource-constrained settings. This
review underscores the importance of developing innovative and context-specific strategies
to enhance forecasting capabilities and plant protection. Future research should focus on
advancing forecasting technologies, addressing data gaps, and adapting systems to evolving
climate conditions to better safeguard food security and environmental sustainability.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author gratefully acknowledges the professional
and moral support provided by the School of Life
Science and Bioengineering (LiSBE) and the Nelson
Mandela African Institution of Science and Technology
(NM-AIST), Arusha – Tanzania.
RESPONSIBLE EDITOR
Anna Tratwal
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have declared that no conflict of interests exist.
REFERENCES (54)
1.
Adhikari D., Pandit V., Bhatta M., Sharma D.R, Baral S. 2024. Plant clinic in Nepal: An overview. Acta Agraria Debreceniensis 1: 5–10. DOI: 10.34101/actaagrar/1/13643.
2.
Akber M. A., Fang X. 2024. Research Progress on Diseases Caused by the Soil-Borne Fungal Pathogen Rhizoctonia solani in Alfalfa. Agronomy 14 (7): 1483. DOI: doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071483.
3.
Alfred R., Obit J.H., Chin C.P.Y., Haviluddin H., Lim Y. 2021. Towards paddy rice smart farming: a review on big data, machine learning, and rice production tasks. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Enginners (IEEE) Access 9: 50358–50380. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3069449.
4.
Bacci M., Zini C., Idrissa O.A., Burrone S., Tsayabou A., Maïga S.S., Tarchiani V. 2023. Field survey data on the effectiveness of agrometeorological services for smallholder farmers in Niger. Data in Brief 48: 109195. DOI: 109195. 10.1016/j.dib.2023.109195.
5.
Bala R., Kaur J., Tak P.S., Sandhu S.K., Pannu P.P.S. 2022. A model for Tilletia indica (Karnal bunt) –Triticum aestivum (Wheat) system under changing environmental conditions. Indian Phytopathology 75 (3): 723–730. DOI: doi.org/10.1007/s42360-022-00520-w.
6.
Bebber D.P., Castillo Á.D., Gurr S.J. 2022. Modelling the effects of climate change on pests and diseases of major UK crops. Pest Management Science 78 (1): 186–195.
7.
Bernardo-Cravo A. P., Schmeller D. S., Chatzinotas A., Vredenburg V. T., Loyau A. 2020. Environmental factors and host microbiomes shape host–pathogen dynamics. Trends in Parasitology 36 (7): 616–633. DOI: 10.1016/j.pt.2020.04.010.
8.
Bouri M., Arslan K. S., Şahin F. 2023. Climate-smart pest management in sustainable agriculture: Promises and challenges. Sustainability 15 (5): 4592. 10.3390/su15054592 DOI: 10.3390/su15054592.
9.
Chen Y. 2020. The impact of environmental conditions on plant diseases. In D. P. Singh, S. Singh, and R. K. Gupta (Eds.), Environmental Stress and Crop Productivity (pp. 149–170). p. 149–170. In: “Environmental Stress and Crop Productivity”. Academic Press. DOI: doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819597-6.00009-0.
10.
Clarke B., Otto F., Stuart-Smith R., Harrington L. 2022. Extreme weather impacts of climate change: an attribution perspective. Environmental Research: Climate 1 (1): 012001. DOI: doi.org/10.1088/2752-5295/ac6e7d.
11.
Cohen S.P., Leach J.E. 2020. High temperature-induced plant disease susceptibility: more than the sum of its parts. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 56: 235–241. DOI: 10.1016/j.pbi.2020.02.008.
12.
Finger C.E., Moreno-Gonzalez I., Gutierrez A., Moruno-Manchon J.F., McCullough L.D. 2022. Age-related immune alterations and cerebrovascular inflammation. Molecular Psychiatry 27 (2): 803–818. DOI: doi.org/10.1038/s41380-021-01361-1.
13.
Fontúrbel F.E., Nespolo R.F., Amico G.C., Watson D.M. 2021. Climate change can disrupt ecological interactions in mysterious ways: Using ecological generalists to forecast community-wide effects. Climate Change Ecology 2: 100044. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecochg.2021.100044.
14.
Fones H.N., Bebber D.P., Chaloner T.M., Kay W.T., Steinberg G., Gurr S. 2020. Threats to global food security from emerging fungal and oomycete crop pathogens. Nature Food 1 (6): 332–342. DOI: 10.1038/s43016-020-0075-0.
15.
Gowtham H.G., Hema P., Murali M., Shilpa N., Nataraj K., Basavaraj G.L., Amruthesh K.N. 2024. Fungal endophytes as mitigators against biotic and abiotic stresses in crop plants. Journal of Fungi 10 (2): 116. DOI: 10.3390/jof10020116.
16.
Hasanaliyeva G., Si Ammour M., Yaseen T., Rossi V., Caffi T. 2022. Innovations in disease detection and forecasting: a digital roadmap for sustainable management of fruit and foliar disease. Agronomy 12 (7):1707. DOI: 10.3390/agronomy12071707.
17.
Hegedus P.B., Maxwell B. D. 2022. Rationale for field-specific on-farm precision experimentation. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 338: 108088. DOI: 10.1016/j.agee.2022.108088.
18.
Hunjan M.S., Lore J.S. 2020. Climate change: Impact on plant pathogens, diseases, and their management. p. 85–100. In: K. Jabran, S. Florentine, & B. S. Chauhan (Eds.), Crop Protection Under Changing Climate (pp.). Springer Nature. DOI: doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46111-9_7.
19.
Jagathjothi N., Deivamani M., Yuvaraj M., Sathya Priya R., Saranya M., Sharmila R., Anitha R. 2024. Plant pathogen mitigation and adaptation to climate change. p. 53–78. In: “Plant Quarantine Challenges under Climate Change Anxiety” Cham: Springer Nature, Switzerland. DOI: 10.1007/978 3 031 56011 8_3.
20.
Jeger M.J., Pautasso M., Holdenrieder O., Shaw M.W. 2021. Modelling disease spread and control in networks: implications for plant health management. Annual Review of Phytopathology 59: 65–89. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-080519-110506.
21.
Juroszek P., Racca P., Link S., Farhumand J., Kleinhenz B. 2020. Overview of some recent advances in regional and field-scale modeling of plant diseases caused by airborne pathogens. European Journal of Plant Pathology 157 (3): 885–899. DOI: 10.1007/s10658-020-02138-4.
22.
Khan R., Noorpoor A., Ebadi A G. 2022. Effects of air contamination on agriculture. p. 1–16. In: “Sustainable Plant Nutrition Under Contaminated Environments”. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
23.
Kumari A., Dash M., Singh S.K., Jagadesh M., Mathpal B., Mishra P.K., Verma K.K. 2023. Soil microbes: a natural solution for mitigating the impact of climate change. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 195 (12): 1436. DOI: 10.1007/s10661-023-11988-y.
24.
Kumari A., Lakshmi G.A., Krishna G.K., Patni B., Prakash S., Bhattacharyya M. Verma K.K. 2022. Climate change and its impact on crops: A comprehensive investigation for sustainable agriculture. Agronomy 12 (12): 3008. DOI: 10.3390/agronomy12123008.
25.
Kumar S., Meena R.S., Sheoran S., Jangir C.K., Jhariya M.K., Banerjee A., Raj A. 2022. Remote sensing for agriculture and resource management. p. 91–135. In “Natural Resources Conservation and Advances for Sustainability” (Jhariya M.K., Meena R.S., Banerjee A., Meena S.N., eds.). Elsevier. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-822976-7.00007-4.
26.
Kumar P., Kadian K.K., Singh K., Mahapatra S.S. 2021. Alternate hosts of plant pathogens: A critical review. Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences 91 (6): 813–819.
27.
Lv Z., Li F., Lu G. 2020. Adjusting sowing date and cultivar shift improve maize adaptation to climate change in China. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change 25: 87–106. DOI: 10.1007/s11027-019-09861-w.
28.
González-Domínguez E., Caffi T., Rossi V., Salotti I., and Fedele G. 2023. Plant disease models and forecasting: changes in principles and applications over the last 50 years. Phytopathology 113 (4): 678–693. DOI: 10.1094/PHYTO 10 22 0362 KD.
29.
Madenova A., Kokhmetova A., Sapakhova Z., Galymbek K., Keishilov Z., Akan K., Yesserkenov A. 2020. Effect of common bunt infection on agronomic traits and resistance of wheat entries. Research on Crops 21 (4): 791–797. DOI: 10.31830/2348-7542.2020.121.
30.
Mahapatra P., Horriat S., Anand B. S. 2018. Anterior cruciate ligament repair–past, present and future. Journal of experimental orthopaedics, 5, 1-10. DOI:
10.1186/s40634-018-0136-6
31.
McLeish M. J., Fraile A., García‐Arenal F. 2020. Trends and gaps in forecasting plant virus disease risk. Annals of Applied Biology 176 (2): 102–108. DOI: 10.1111/aab.12553.
32.
McRoberts N., Hall C., Madden L.V., Hughes G. 2021. Perceptions of disease risk: From social construction of subjective judgments to rational decision making. Phytopathology 111 (5): 733–744. DOI: 10.1094/PHYTO‑04‑10‑0126.
33.
Mieslerová B., Cook R.T., Wheater C.P., Lebeda A. 2022. Ecology of powdery mildews–influence of abiotic factors on their development and epidemiology. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences 41 (6): 365–390. DOI: 10.1080/07352689.2022.2138044.
34.
Moura A.B., Backhouse D., de Souza Júnior I.T., Gomes C.B. 2022. Soilborne pathogens. p. 199–224. In: “Subsoil Constraints for Crop Production”. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
35.
Nakalembe C., Becker-Reshef I., Bonifacio R., Hu G., Humber M.L., Justice C.J., Sanchez A. 2021. A review of satellite-based global agricultural monitoring systems available for Africa. Global Food Security 29: 100543. DOI: 10.1016/j.gfs.2021.100543.
36.
Phour M., Sindhu S.S. 2023. Soil salinity and climate change: microbiome-based strategies for mitigation of salt stress to sustainable agriculture. p. 191-243. In: “Climate Change and Microbiome Dynamics: Carbon Cycle Feedbacks”. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
37.
Quamar M M., Al-Ramadan B., Khan K., Shafiullah M., El Ferik S. 2023. Advancements and applications of drone-integrated geographic information system technology: A review. Remote Sensing 15 (20): 5039. DOI: 10.3390/rs15205039.
38.
Rai A., Irulappan V., Senthil-Kumar M. 2022. Dry root rot of chickpea: a disease favored by drought. Plant Disease 106 (2): 346–356. DOI: 10.1094/PDIS-07-21-1410-FE.
39.
Sarkar A., Wang H., Rahman A., Memon W.H., Qian L. 2022. A bibliometric analysis of sustainable agriculture: based on the Web of Science (WOS) platform. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 29 (26): 38928–38949. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-022-19632-x.
40.
Satheesh Naik S.J., Bohra A., Basavaraja T., Mishra R.K., Padmaja G., Poornima K.N. 2020. Diversity of Phytophthora stem blight of pigeonpea and its sustainable management. p. 121–130. In: “Management of Fungal Pathogens in Pulses: Current Status and Future Challenges” (Garima S., Krishna K., Chandra Nayak S., Srinivasa N., eds.). Springer Nature.
41.
Sharma G. D., Thomas A., Paul J. 2021. Reviving tourism industry post-COVID-19: A resilience-based framework. Tourism Management Perspectives 37: 100786. DOI: doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2020.100786.
42.
Shokory J.A., Schaefli B., Lane S.N. 2023. Water resources of Afghanistan and related hazards under rapid climate warming: a review. Hydrological Sciences Journal 68 (3): 507–525. DOI: 10.1080/02626667.2022.2159411.
43.
Singh R. 2022. Strategies for the management of plant diseases. Journal of Integrated Pest Management 13 (1): 1–14. DOI: 10.1093/jipm/pmac005.
44.
Singh B. K., Delgado-Baquerizo M., Egidi E., Guirado E., Leach J. E., Liu H., Trivedi P. 2023. Climate change impacts on plant pathogens, food security and paths forward. Nature Reviews Microbiology 21 (10): 640–656. DOI: 10.1038/s41579-023-00888-6.
45.
Smith F., Luna E. 2023. Elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide and plant immunity to fungal pathogens: do the risks outweigh the benefits? Biochemical Journal 480 (22): 1791–1804. DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20230152.
46.
Sreeshna T.R., Athira P., Soundharajan B. 2024. Impact of climate change on regional water availability and demand for agricultural production: application of water footprint concept. Water Resources Management: 1–33. DOI: 10.1007/s11269-024-03839-3.
47.
Tenllado F., Canto T. 2020. Effects of a changing environment on the defenses of plants to viruses. Current Opinion in Virology 42:40-46.
48.
Thines M., Carver T. L. W., Müller-Stöver D. 2021. Drought-induced changes in root exudates and soil microbial communities: Implications for potato disease management. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 161: 108381. DOI: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108381.
49.
Verma K.K., Song X.P., Kumari A., Jagadesh M., Singh S.K., Bhatt R., Li Y.R. 2024a. Climate change adaptation: Challenges for agricultural sustainability. Plant, Cell & Environment. DOI: doi.org/10.1111/pce.15078.
50.
Verma K. K., Joshi A., Song X. P., Liang Q., Xu L., Huang H. R., Li Y. R. 2024b. Regulatory mechanisms of plant rhizobacteria on plants to the adaptation of adverse agroclimatic variables. Frontiers in Plant Science 15: 1377793.
51.
Verma K. K., Song X. P., Yadav G., Degu H. D., Parvaiz A., Singh M., Li, Y. R. 2022. Impact of agroclimatic variables on proteogenomics in sugar cane (Saccharum spp.) plant productivity. ACS Omega 7 (27): 22997–23008.
52.
Verma K. K., Singh P., Song X. P., Malviya M. K., Singh R. K., Chen G. L., Li Y. R. 2020a. Mitigating climate change for sugarcane improvement: role of silicon in alleviating abiotic stresses. Sugar Tech 22: 741–749.
53.
Verma K.K., Song X.P., Li D.M., Singh M., Rajput V.D., Malviya M.K., Li Y.R. 2020b. Interactive role of silicon and plant–rhizobacteria mitigating abiotic stresses: A new approach for sustainable agriculture and climate change. Plants 9 (9): 1055.
54.
Yadav N., Monika K., Kumar N., Mamta H., Arya S.S. 2022. Impacts on plant growth and development under stress. p. 61–100. In: “Plant Stress Mitigators: Action and Application” (A. Vaishnav, S.S. Arya, D.K. Choudhary, eds.). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.